# 异步组件
以前的写法
const asyncPage = () => import("./NextPage.vue");
现在要放在defineAsyncComponent方法内
const asyncPage = defineAsyncComponent(() => import("./NextPage.vue"));
# Composition API
# setup
入口函数,
Composition API在此函数中使用
props: 用来接收props数据context用来定义上下文, 上下文对象中包含了一些有用的属性,这些属性在vue 2.x中需要通过this才能访问到, 在 setup() 函数中无法访问到 this,是个undefined- 返回值:
return {}, 返回响应式数据,template模版中需要使用的变量、函数
setup(props, context) {
context.attrs
context.slots
context.parent
context.root
context.emit
context.refs
return {
}
}
# ref
创建一个响应的数据对象,通过
value属性进行set和get值。当然,模板直接调用即可
<template>
<div @click="handleClick">{{ name }}</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const name = ref("gauhar");
const handleClick = () => {
name.value = "gauharchan";
};
return {
name,
handleClick,
};
},
};
</script>
# reactive
该函数接收一个对象,创建返回一个响应式对象。
通常搭配
toRefs函数转换为一个个ref响应式数据,在返回出去,在模板中正常使用。如果直接返回state,在模板中state.xxx调用不可直接解构属性使用,否则会丢失响应式。如需解构,请使用
toRefs转化后再解构
<script>
import { reactive, toRefs } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const state = reactive({
decs: "书本中有农场,抬头只得操场",
count: 0,
});
const { count } = state; // 丢失响应性😭
const { count } = toRefs(state); // 😁 此时count是一个ref,所以后面使用需要count.value
return {
...toRefs(state),
};
},
};
</script>
# watch
注意
watch() 和 watchEffect() 在 DOM 挂载或更新之前运行副作用(回调函数),所以当侦听器运行时,模板引用还未被更新。
监听reactive对象中的某一项,watch的第一个参数用函数返回那一项。或者使用toRefs转换为ref对象
const state = reactive({
name: "",
});
// 使用函数返回
watch(
() => state.name,
(newVal, oldVal, onInvalidate) => {
console.log(newVal, oldVal, "watch");
}
);
// 使用toRefs
watch(toRefs(state).name, (newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log(newVal, oldVal, "watchBytoRefs");
});
state.name = "gauhar";
所以如果要监听的是ref对象,直接写即可
let num = ref(0);
watch(num, (newVal, oldVal, onInvalidate) => {
console.log(newVal, oldVal, "watch1"); // 123 0
});
num.value = 123;
提示
注意watchCallback的第三个参数是onInvalidate,详情请看
# 同时监听多个
注意,回调函数的参数,第一个数组是所监听对象的新值的数组(
newNum,newCount)。第二个数组是旧值的数组监听多个时,只要有一个更新就会触发,如下面的 num
注意多个同步更改只会触发一次侦听器。
const state = reactive({
count: 456,
});
let num = ref(0);
watch([num, toRefs(state).count], ([newNum, newCount], [oldNum, oldCount]) => {
console.log(newNum, oldNum, "watchNum");
console.log(newCount, oldCount, "watchCount");
});
num.value = 123;
停止监听
执行
watch返回的函数即可
# 监听 props 的变化
对于组件的
props对象,他是响应式的;watch监听整个props的改变没有问题。但是监听props的属性直接watch是不可行的
❎ 错误示范
直接 props. 某个属性,或者说直接从 props 中解构出来监听是不行的。
watch(props.dataList, (newVal) => {
console.log("newVal", newVal);
});
✅正确姿势
1.使用 computed 返回指定属性 2.使用 toRefs 转换整个 props
// 1.使用computed返回指定属性
const dataList = computed(() => props.dataList);
watch(dataList, (newVal) => {
console.log("newVal", newVal);
});
// 2.使用toRefs转换整个props
const { dataList } = toRefs(props);
watch(dataList, (newVal) => {
console.log("newVal", newVal);
});
# watchEffect
watch()和watchEffect()在 DOM 挂载或更新之前运行副作用(回调函数),所以当侦听器运行时,模板引用还未被更新。
与watch不同的是
- 不需要指定监听的变量,在
watchEffect的回调中使用了哪些变量就会监听哪些变量 - 也正因为第一点,在初始化的时候会执行一次收集依赖(回调中使用的变量)
- 拿不到新旧值
# 监听的东西一定是要具体到值
否则在页面第一次收集依赖的时候会执行。后面数据改变后不响应。
回调中只监听 ref 或 reactive 中的属性(ref 不包含 ref.value)
import { computed, reactive, watch, watchEffect } from "vue";
import { useStore } from "vuex";
const store = useStore();
let date = computed(() => store.state.date); // date: {startTime: '2020-01'}
watchEffect(() => {
console.log("date", date); // 🙁x
// 具体到里面的startTime
console.log(date.value.startTime); // 😁√
});
ref 的例子
const obj: any = ref({
aa: {
sum: 1,
},
});
watchEffect(() => {
console.log("obj.aa", obj.value); // 🙁x
// 具体到里面的aa
console.log("obj.aa", obj.value.aa); // 😁√
});
# onInvalidate()
过期钩子函数,他的执行时机是**“在 watch 内部每次检测到变更后,在副作用函数重新执行之前”**
onInvalidate(fn)传入的回调会在 watchEffect 重新运行或者 watchEffect 停止的时候执行
常用于在WatchCallback中控制异步操作,比如在callback中发起请求,触发了两次watch,也就是触发了两次请求,一般情况下,我们只关心最后一次的结果,那么就可以在这个函数中取消请求
watchEffect((onInvalidate) => {
// 异步api调用,返回一个操作对象
const apiCall = someAsyncMethod(props.userID);
onInvalidate(() => {
// 取消异步api的调用。
apiCall.cancel();
});
});
上面提到的模板引用,如果想修改这个默认的行为,可以传递第二个参数更改
- flush
- 'pre': 默认值,组件更新前触发副作用
- 'post': 组件更新后触发副作用
- 'sync': 组件更新同步触发副作用
// 在组件更新后触发,这样你就可以访问更新的 DOM。
// 注意:这也将推迟副作用的初始运行,直到组件的首次渲染完成。
watchEffect(
() => {
/* ... */
},
{
flush: "post",
}
);
# 3.2 新增
watchPostEffect和watchSyncEffect别名代替flush选项也可用于使代码意图更加明显。
# 新的生命周期
在
setup函数中使用vue3 取消了
beforeCreate和created,由setup函数代替
import { set } from "lodash";
import {
defineComponent,
onBeforeMount,
onBeforeUnmount,
onBeforeUpdate,
onErrorCaptured,
onMounted,
onUnmounted,
onUpdated,
} from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
setup(props, context) {
onBeforeMount(() => {
console.log("beformounted!");
});
onMounted(() => {
console.log("mounted!");
});
onBeforeUpdate(() => {
console.log("beforupdated!");
});
onUpdated(() => {
console.log("updated!");
});
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
console.log("beforunmounted!");
});
onUnmounted(() => {
console.log("unmounted!");
});
onErrorCaptured(() => {
console.log("errorCaptured!");
});
return {};
},
});
# 节点的 ref
this.$ref.xxx这个在 vue2 也是很经常使用
watch()和watchEffect()在 DOM 挂载或更新之前运行副作用(回调函数),所以当侦听器运行时,模板引用还未被更新。
- 创建一个
ref对象,初始化为null - return 出去
- 在
template节点中绑定 - 通过
.value使用
<template>
<audio
controls
ref="audio"
src="http://gauhar.top/music/static/media/%E6%9E%97%E4%BF%8A%E6%9D%B0-%E9%9B%AA%E8%90%BD%E4%B8%8B%E7%9A%84%E5%A3%B0%E9%9F%B3.ff6502e.mp3"
loop
></audio>
</template>
<script>
import { onMounted, reactive, ref } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const audio = ref(null);
onMounted(() => {
console.log(audio.value); // 原生dom
});
return {
audio,
};
},
};
</script>
# 绑定全局变量
在
main.js中,通过实例的config.globalProperties绑定全局变量
import { createApp } from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
import "./index.css";
const app = createApp(App);
app.config.globalProperties.$message = "123";
app.mount("#app");
在页面中通过config.globalProperties的ctx获取
const { ctx: that }: any = getCurrentInstance();
console.log(that.$message); // 123
但是,在 setup 中不可以调用 getCurrentInstance().ctx 来获取组件内部数据,因为在 prod 会被干掉
推荐使用proxy获取,无论开发还是生产环境都可以获取到
const that: any = getCurrentInstance()?.proxy;
console.log(that.$message); // 123
# TreeShaking
摇树优化。是通过编译器**(
webpack等打包工具)**进行的,把没有用到的东西剔除掉。依赖es6的模块化的语法,将无用的代码(dead-code)进行剔除!使得最后打出来的包体积更小
# reactive 代替 vuex
很多时候只是为了组件之间通信、有个全局的响应数据可以获取。都用 vuex,就会显得有点大材小用的意思
和vuex一样,state中定义变量。mutation定义逻辑方法,通过mutation的方法去改变state中的值
// store/state.js
export default {
name: "gauhar",
};
// store/mutation.js
export default {
setName(state, value) {
// do something
state.name = value + "commit";
},
};
store/index.js
- 通过
reactive将state转为响应式数据,所以更改state中的变量之后,页面中就可以拿到最新的值 - 对外抛出的
state使用readonly包住,防止直接修改state的数据。换而言之,只能通过mutation的方法去更改变量的值 commit方法接收两个参数,第一个是mutation.js中的函数名第二个是新的值
import data from "./state";
import mutation from "./mutation";
import { readonly, reactive } from "vue";
const reactiveData = reactive(data);
export const commit = (fn, value) => {
mutation[fn](reactiveData, value); // 把可更改的响应数据给mutation
};
export const state = readonly(reactiveData);
main.js
- 使用
provide往后代组件推
import { createApp } from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
import { state, commit } from "./store";
import "./index.css";
const app = createApp(App);
app.provide("state", state);
app.provide("commit", commit);
app.mount("#app");
后代任意组件通过inject调用
let storeData: any = inject('state')getlet commit: any = inject('commit')set
<template>
<div @click="handleLogText">{{ isRefText }}</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { unref, ref, Ref, inject, defineComponent } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
let storeData: any = inject("state");
let commit: any = inject("commit");
const isRefText: string = "click me";
const handleLogText = () => {
commit("setName", "apiComponent");
console.log(storeData.name, "apiComponent");
};
return {
isRefText,
handleLogText,
};
},
});
</script>
# vuex
# 获取store对象
- option api 还是一样可以通过
this.$store - composition api,通过
const that = getCurrentInstance()?.proxy拿到实例,that.$store访问 - 再则就是通过
useStore获取。const store = useStore()。store.state.....,store.commit()....
# 页面中使用 state 的变量
通过 computed 返回,否则出现不响应的情况
<template>
<div>
{{ date.startTime }}
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed } from "vue";
import { useStore } from "vuex";
const store = useStore();
let date = computed(() => store.state.date);
</script>
# setup 语法糖
直接定义变量,模板使用即可
<script setup lang="ts">
const name = ref("gauhar");
const info = reactive({
age: 18,
});
</script>
从vue中解构出defineEmit, defineProps
const props: Iprop = defineProps({
filterData: {
type: Object,
default: () => ({}),
},
form: {
type: Object,
default: () => ({}),
},
});
console.log(props.form);
// 数组中的值就是自定义事件名
const emit = defineEmit(["confirm", "reset", "search"]);
# TS 配合 defineProps 使用
在
ts中声明props主要涉及到的问题就是类型声明。
原始语法中,type 的类型选项是 js 的类型,比如:String、Object。在 ts 的使用中并不满足。举个 🌰,定义一个Object类型,同时指定里面的属性的类型。或许会使用类型断言
interface IFilter {
a?: string;
}
const props: Iprop = defineProps({
filterData: {
type: Object as IFilter,
default: () => ({}),
},
});
实际上vue3也是推出了针对ts的api
# 使用泛型声明
单纯这么写有个缺点,不能声明默认值
const props1 = defineProps<{
filterData: any;
}>();
如果想指定默认值,那么就通过withDefaults编译器宏配合使用
第一个参数是定义
props,第二个参数是默认值
interface Props {
msg?: string;
labels?: string[];
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
msg: "hello",
labels: () => ["one", "two"],
});
# 调试
# console
其实
vue3内部实现了一个initCustomFormatter让我们在开发模式下更加直观美化的展示我们打印的东西
比如打印一个ref对象
未开启功能前
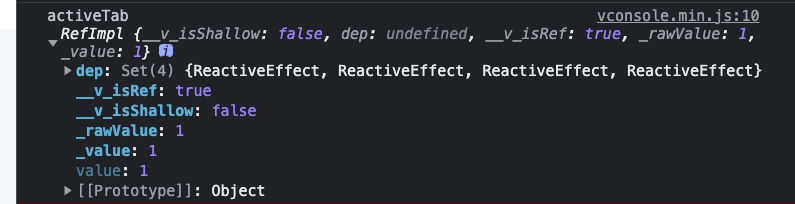
像我这个强迫症,我是一定会把那个未展开的 value 点一下的 😄
开启后
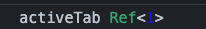
非常直观,知道是一个 ref,然后值是 1
一般情况下,我们只关心这个ref的value,而不关心他身上的一些其他标识,比如上面的__v_isRef 、__v_isShallowReactiveFlags;这两个标识分别是
- 是否为
ref对象 - 是否为浅层代理
_rawValue: 原始数据
# 开启美化方法
摘录来自 Vue.js 设计与实现 霍春阳(HcySunYang)
“以 Chrome 为例,我们可以打开 DevTools 的设置,然后勾选“Console”→“Enable custom formatters”选项”
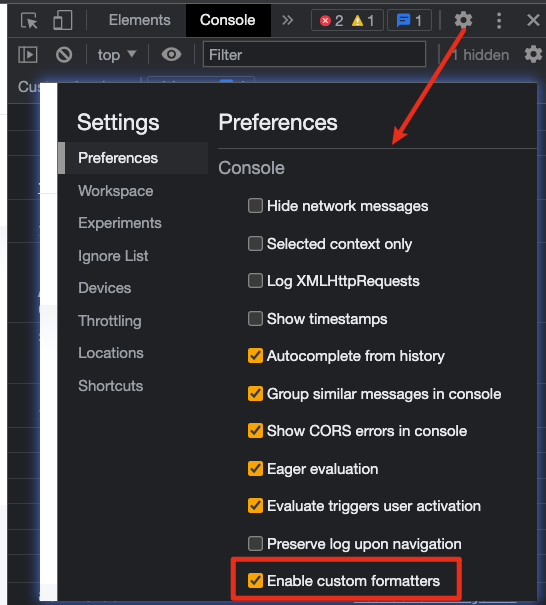
然后刷新即可使用 😎
# 路由
import { useRoute, useRouter } from "vue-router";
const route = useRoute();
const router = useRouter();
console.log(route.query);
router.back();
// 监听完整的路由,包括hash、query
watch(
() => route.fullPath,
(newVal, prevVal) => {
noBar.value = ["/login", "/error"].includes(newVal);
}
);
# vite 配置
配置别名的时候,注意一下,是
/@变量的命名和
vue/cli不同,以VITE开头VITE_ENUMS使用的框架、插件必须在
optimizeDeps的include中声明
import { defineConfig } from "vite";
import vue from "@vitejs/plugin-vue";
import { resolve } from "path";
const Enums = require("./src/enums/index");
process.env.VITE_ENUMS = JSON.stringify(Enums);
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vue()],
alias: {
"/@": resolve(__dirname, "src"),
},
optimizeDeps: {
include: [
"js-md5",
"moment",
"ant-design-vue/es/locale/zh_CN",
"@ant-design/icons-vue",
],
},
});
# 文档
# unRef
语法糖,如果传入的参数是
ref对象,就返回参数.value,否则返回本身。
val = isRef(val) ? val.value: val
调用getText方法,无论是普通的变量还是响应式数据,都可以正确的得到文本
function getText(val?: string | Ref<string>) {
return unref(val);
}
# Teleport
将子元素渲染到指定的父元素,常用的是一个组件调用打开
modal弹窗,然后让这个modal渲染在body下,而不是组件下
下面的modal本来是在modal-box里面的,teleport将他传送到body
<template>
<div class="modal-box">
<button @click="handleOpen('.modal-box')">组件里</button>
<button @click="handleOpen('body')">body</button>
<teleport :to="dom">
<div v-if="modalOpen" class="modal">
<div>
这是一个模态窗口! 我的父元素是"body"!
<button @click="modalOpen = false">Close</button>
</div>
</div>
</teleport>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, toRefs } from "vue";
export default {
setup() {
const state = reactive({
modalOpen: false,
dom: "body",
});
const handleOpen = (dom) => {
state.dom = dom;
state.modalOpen = true;
};
return {
...toRefs(state),
handleOpen,
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.modal {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.modal div {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
background-color: white;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
padding: 5px;
}
.modal-box {
position: relative;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
</style>
# emits
子组件中
emit触发父组件的函数的自定义事件名,需要在emits选项中声明
**如果没有在emits声明,则监听的事件挂载在组件的根节点上。**这也是去除.native修饰符的原因
子组件
<div :class="prefixCls" @click="$emit('click')">button</div>
父组件
<Button @click="handleClickButton" />
<script>
function handleClickButton() {
console.log("11111", 11111);
}
</script>
点击的时候,会触发两次!
# 组件 v-model
父组件
v-model:+别名。默认的名字是modelValue。事件名:update:modelValue父组件这边绑定一个变量
<ComA v-model:text="iputText" v-model:content="iputContentText">
<template #box>
slot111323232321
</template>
</ComA>
<div>{{iputText}}</div>
<div>{{iputContentText}}</div>
子组件
子组件这边
props接收别名,通过emits指定触发事件名如果不指定
emits,就会收到一个警告
<template>
<div>text</div>
<input type="text" @input="handleInput" />
<div>content</div>
<input type="text" @input="handleContentInput" />
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
text: String,
content: String,
},
emits: ["update:text", "update:content"],
setup(props, { emit }) {
function handleInput(e) {
emit("update:text", e.target.value);
}
function handleContentInput(e) {
emit("update:content", e.target.value);
}
return {
handleInput,
handleContentInput,
};
},
};
</script>
# defineAsyncComponent
异步组件要求使用
defineAsyncComponent方法创建
import { defineAsyncComponent } from "vue";
// 不带配置的异步组件
const asyncPage = defineAsyncComponent(() => import("./NextPage.vue"));
如果要配置
import ErrorComponent from "./components/ErrorComponent.vue";
import LoadingComponent from "./components/LoadingComponent.vue";
// 待配置的异步组件
const asyncPageWithOptions = defineAsyncComponent({
loader: () => import("./NextPage.vue"), // component
delay: 200,
timeout: 3000,
errorComponent: ErrorComponent,
loadingComponent: LoadingComponent,
});
# 按键修饰符
不再支持使用数字 (即键码) 作为
v-on修饰符不再支持全局配置的
config.keyCodes
<input type="text" @keydown.13="handleContentInput"> // don't work
<input type="text" @keydown.enter="handleContentInput"> // 😁right
# 过渡类名
v-enter→v-enter-fromv-leave→v-leave-from
# css
# 深度(穿透)选择器
在父组件中覆盖子组件的样式时,如果父组件是局部样式
(scoped)会出现无法修改的情况。这时得用更深的选择器等大多数用户迁移 vue3 后,将会弃用
/deep/、>>>。vue3 中改为:deep(css选择器)
:deep(.blue) {
color: green;
}
# Provide / Inject
如果
provide响应式数据,则应该使用readOnly包裹,避免污染。所有的更改应该由提供provide的组件维护。修改值的方式:
provide一个修改方法,在Inject的组件中调用此方法进行过修改,而不是直接修改
// 父组件
import { defineComponent, provide, readonly, ref } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const name = ref("gauhar");
const updateName = (value) => {
name.value = value;
};
provide("name", readonly(name));
provide("updateName", updateName);
},
});
// 子组件
import { defineComponent, inject } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const name = inject("name");
const updateName: any = inject("updateName");
return {
name,
updateName,
};
},
});
# computed
# Computed Debugging
开发环境下的
computed调试。3.2新增
新增了第二个参数
onTrack收集依赖时触发onTrigger依赖改变时(更新时)触发
const plusOne = computed(() => count.value + 1, {
onTrack(e) {
// triggered when count.value is tracked as a dependency
debugger;
},
onTrigger(e) {
// triggered when count.value is mutated
debugger;
},
});
// access plusOne, should trigger onTrack
console.log(plusOne.value);
// mutate count.value, should trigger onTrigger
count.value++;